What is India, Who discovered India
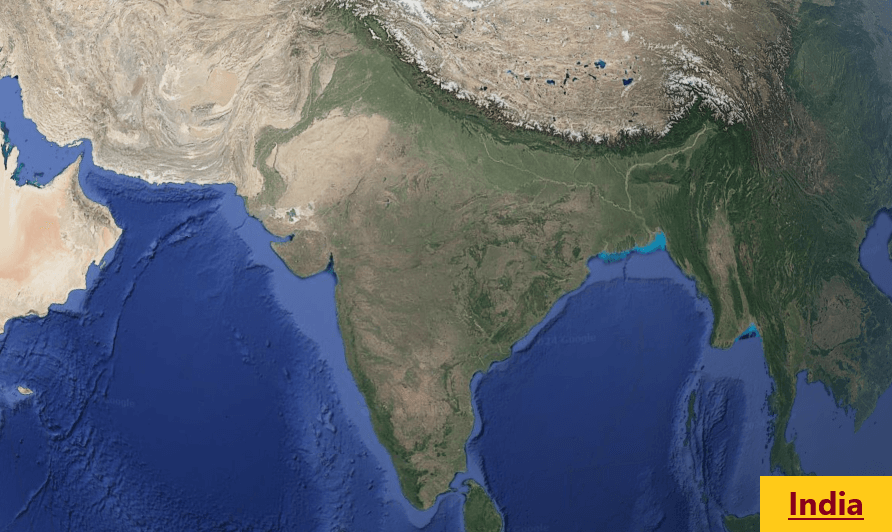
India is a country rich in diversity and cultural heritage, often referred to as the “Land of Gold.” Located in the southern part of the Asian continent, it is surrounded by oceans on three sides: the Bay of Bengal to the east, the Arabian Sea to the west, and the Indian Ocean to the south. With an area of approximately 3.3 million square kilometers, India ranks as the seventh-largest country in the world. Its population is around 1.4 billion, making it the most populous country globally, What is India, Who discovered India.
The culture of India is extremely diverse, encompassing various religions, languages, and traditions. People from different faiths such as Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Christianity, and Jainism coexist harmoniously. Hindi is the official language of India, but there are a total of 22 recognized languages spoken across the country. The phrase “Unity in Diversity” encapsulates India’s identity, where people from different backgrounds live together peacefully.
India’s history is also remarkable; it is known as the birthplace of ancient civilizations and has been home to renowned educational institutions like Takshashila and Nalanda. After gaining independence from British rule in 1947, India adopted a democratic system where leaders are elected by the people. Today, it stands as a significant economic power with advancements in technology, agriculture, and industry, What is India, Who discovered India.
Geographically, India features a wide range of landscapes from the Himalayan mountain range to tropical beaches. Major rivers like the Ganges, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra flow through its land. India is famous for its historical sites such as the Taj Mahal, Red Fort, and Golden Temple, making it a key tourist destination. In summary, India is an incredible nation known for its cultural heritage, natural beauty, and historical significance on a global scale.
What is the history of india
India’s history is a rich and diverse journey that spans thousands of years. It began around 65,000 years ago with the arrival of Homo sapiens, who migrated from Africa to the Indian subcontinent. Following this, the Indus Valley Civilization developed between approximately 2500 and 1900 BCE, recognized as South Asia’s first urban culture.
In ancient India, the Vedic civilization emerged, significantly influenced by Aryan culture. The Aryans arrived in the Indian subcontinent around 2000 BCE, laying the foundations of the Sanskrit language and Vedic religion. This period saw the rise of various republics and monarchies, such as Magadha and Kaushambi, which played crucial roles in political and cultural development.
The medieval period in India was marked by Islamic invasions that brought significant changes. By the late 12th century, the Delhi Sultanate was established, followed by the rise of the Turkic and Mughal empires. Babur invaded India in 1526, founding the Mughal Empire, which ruled for the next three centuries.
The modern era began with the arrival of British imperialism. The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a significant uprising against British rule, leading to India’s independence in 1947. Mahatma Gandhi’s non-violent movement was pivotal in uniting Indian society during this struggle. Today, India is a democratic nation known for its diverse cultural heritage and rich history, What is India, Who discovered India.
How was india formed
India’s establishment and development is a long and complex story influenced by historical, social, and economic factors.
Early History
India’s history begins with ancient civilizations, notably the Indus Valley Civilization (around 2500 BCE). Following this, various empires emerged, such as the Maurya and Gupta Empires, which made significant contributions to art, science, and culture.
Colonial Period
The arrival of British rule in the late 18th century drastically changed India’s political and economic structure. British governance weakened India’s economy, leading to a significant transfer of wealth to Britain. During this period, the Indian independence movement fostered a spirit of freedom among the populace.
Post-Independence
In 1947, India gained independence from British rule. This marked a new beginning with the creation of the Indian Constitution, which established the principles of democracy, equality, and justice.
Economic Development
After independence, India focused on industrialization and the Green Revolution. The economic liberalization in 1991 strengthened India’s position in the global market. Today, India is considered the sixth-largest economy in the world and is recognized as an emerging superpower, How was india formed.
Who discovered India and how
Vasco da Gama’s discovery of India is typically associated with the year 1498, when he first set foot in Calicut (now Kozhikode). This journey was aimed at finding a sea route from Europe to India, and it led to the spread of knowledge about India across Europe. During his visit, da Gama observed India’s wealth and resources, providing detailed accounts that contributed to the perception that he had “discovered” India, Who discovered India and how.
How is the climate of India
India’s climate is primarily monsoonal, divided into four main seasons: winter, summer, monsoon, and autumn. This climate is determined by geographical location, landforms, and prevailing winds. India is situated between 8°4′ and 37°6′ north latitude, and the presence of the Himalayas significantly influences its climate by blocking cold winds from the north and aiding the monsoon winds in bringing rainfall to the region.
Most of India’s rainfall occurs between June and September when the southwest monsoon is active. During this time, regions like Assam, Meghalaya, and Konkan experience heavy rainfall, while areas such as Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan receive less precipitation. The temperature distribution in India is also diverse; northern India experiences a greater temperature range compared to the southern regions, What is India, Who discovered India.
What is the development level of India, which is the most developed state of India
India’s development level has rapidly increased over the past few decades, establishing it as an emerging economy on the global stage. Approximately 21% of India’s economy is derived from agriculture, another 21% from industry, and 48% from the service sector, providing a diverse and balanced economic structure.
Maharashtra is the most developed state in India, with a Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of around 42.67 lakh crore (US$430 billion). This state is home to Mumbai, India’s financial capital, and serves as a major hub for manufacturing, trade, and finance. Many multinational corporations have their headquarters in Maharashtra, which plays a crucial role in the country’s maritime trade. Following Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu and Gujarat rank second and third, with GSDPs of 31.55 lakh crore and 27.9 lakh crore, respectively.
Other prosperous states include Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka, with GSDPs of 24.99 lakh crore and 28.09 lakh crore. These states have also made significant progress in their respective sectors, contributing to India’s overall economic growth, What is India, Who discovered India.
What is the status of technology in India
India’s development level and technological status are both critical subjects that reflect the country’s economic and social progress.
Development Level
India has made remarkable advancements in various sectors over the past few decades. Currently, the literacy rate in India is approximately 74.04%, a significant increase from just 12% at the time of independence. The country has also achieved notable milestones in science and technology, including successes in space programs and an increase in scientific publications, where India now ranks third globally, following China and the United States. Additionally, India boasts over 125,000 startups and 110 unicorns, making it the third-largest startup ecosystem after the US and China.
Technological Level
The technological landscape in India is rapidly evolving. The IT industry has surpassed $250 billion and is projected to reach between $300 billion and $350 billion in the next five years. The telecommunications sector is also significant, being the second-largest in the world with 1.1 billion subscribers. India has made strides in areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cybersecurity; however, there remains a challenge due to a lack of specialized skills in these fields, What is India, Who discovered India.
What are the seven wonders of india
India’s seven wonders are symbols of the country’s rich culture and remarkable architectural artistry. These wonders are located in various states and are renowned for their historical significance.
- Taj Mahal (Agra, Uttar Pradesh): Built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal, this white marble mausoleum is not only India’s most famous monument but also a global icon. Construction took place between 1632 and 1648, and it is regarded as a symbol of love.
- Golden Temple (Amritsar, Punjab): Known as Harmandir Sahib, this is the holiest site in Sikhism. Its golden dome and surrounding sacred pond make it unique. Built between 1577 and 1604, it serves as a center of religious and cultural importance.
- Konark Sun Temple (Odisha): Constructed in the 13th century, this temple is dedicated to the Sun God and is designed like a massive chariot. Its intricate carvings and architecture make it an extraordinary monument.
- Khajuraho (Madhya Pradesh): Famous for its erotic sculptures, the temples were built by the Chandela dynasty between 950 and 1050 AD. These sculptures showcase the diversity and richness of Indian art.
- Nalanda University (Bihar): Once a major center of education in ancient times, this university was known for studying Buddhism and philosophy. It was established between 427 and 1197 AD and is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Hampi (Karnataka): The former capital of the Vijayanagara Empire, Hampi features a vast complex of ancient temples, palaces, and forts. Its historical significance and architecture make it special.
- Gommateshwara Temple (Shravanabelagola, Karnataka): This important Jain pilgrimage site is home to a 57-foot tall statue of Lord Rishabhadeva carved from a single granite rock. It exemplifies exceptional artistry.
These seven wonders not only represent India’s historical heritage but have also become symbols of Indian culture worldwide, What are the seven wonders of india.
What are the major languages of India and what is the mother tongue of India
India is a multilingual country where 22 major languages are recognized under the Constitution. These include Hindi, Bengali, Marathi, Telugu, Tamil, Gujarati, Urdu, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Punjabi, Sindhi, Kashmiri, Maithili, Santhali, among others.
Hindi is the most widely spoken language in India, with approximately 528.3 million people identifying it as their mother tongue according to the 2011 census. This accounts for about 43.63% of the total population. Hindi is primarily spoken in northern India and has several dialects such as Awadhi, Braj, and Khadi Boli.
While Hindi is given prominence as a mother tongue in India, other languages also hold significant importance. Bengali is spoken by around 97.2 million people, Marathi by about 83 million, Telugu by approximately 81.1 million, and Tamil by roughly 69 million. These languages are used across various states and are integral to Indian culture, What are the major languages of India.
What are the major religions of India
India is a country rich in religious diversity, where various religions are practiced. The major religions include Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Christianity, Jainism, and Buddhism.
Hinduism is the largest and oldest religion in India, with about 80% of the population adhering to it. It is also known as Sanatana Dharma and has sacred texts such as the Vedas, Upanishads, Ramayana, and Bhagavad Gita. Temples play a significant role in Hindu worship, and festivals like Diwali, Holi, and Durga Puja are widely celebrated.
Islam is the second-largest religion in India, comprising around 13% of the population. The Quran is its holy book, and followers adhere to the teachings of Prophet Muhammad. Major Islamic festivals include Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha.
Sikhism was founded by Guru Nanak in the 15th century and is primarily practiced in the Punjab region. Sikhs regard the Guru Granth Sahib as their holy scripture and emphasize principles of service and equality.
Christianity, followed by about 2.3% of the population, is based on the teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians celebrate festivals like Christmas.
Jainism emerged during the time of Mahavira and is based on principles of non-violence and truth. Jains believe that self-purification leads to the liberation of the soul.
Buddhism, established by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha), also holds an important place in India. It emphasizes meditation and practices compassion and non-violence.
In addition to these major religions, India is home to Zoroastrians, Jews, and various local religious practices that reflect its rich religious tapestry, What is India, Who discovered India.
Which country exports most to India, Which country imports the most to India
India’s trade is widely spread across various countries, including both exports and imports. In terms of exports, the United States is India’s largest trading partner, accounting for approximately 15.88% of India’s total exports. Following the U.S., the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and China contribute 9.13% and 5.07%, respectively.
On the other hand, when it comes to imports, China is the largest source for India, making up about 15.42% of total imports. Other significant import sources include Russia, the UAE, the United States, and Iraq. In the fiscal year 2023-24, India imported goods worth $56.29 billion from China and exported $40.38 billion to the United States.
The main imported items in India include crude oil, gold, electronic equipment, and industrial machinery. In contrast, major exports consist of petroleum products, gemstones and jewelry, and engineering goods, What is India, Who discovered India.
Which are the neighbouring countries of india
India shares its borders with a total of nine neighboring countries. Among these, seven countries have land borders with India, while two countries are separated by sea.
- Afghanistan: The border with Afghanistan is located in Jammu and Kashmir (specifically the part known as POK), and it is approximately 106 kilometers long.
- Bangladesh: Situated to the east of India, Bangladesh shares a lengthy border of about 4096.7 kilometers, connecting through the Indian states of West Bengal, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Assam.
- Bhutan: This small country in the northern region has a border length of around 699 kilometers, adjoining the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Sikkim, and West Bengal.
- China: A significant neighbor, China shares a border of approximately 3488 kilometers with India, touching regions including Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Myanmar: The eastern border with Myanmar is about 1643 kilometers long and connects through Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland.
- Nepal: Nepal’s border with India extends approximately 1751 kilometers, linking through the states of Sikkim, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
- Pakistan: To the west, Pakistan shares a border of about 3323 kilometers, which connects through Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Gujarat, and Rajasthan.
Additionally, India has maritime boundaries with Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Sri Lanka is separated from India by the Gulf of Mannar to the southeast, while the Maldives lies to the southwest beneath the Lakshadweep Islands. The relationships India maintains with these neighboring countries are crucial from cultural, historical, and strategic perspectives, Which are the neighbouring countries of india.
How many states are there in India
India has a total of 28 states and 8 union territories. The list of states includes:
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chhattisgarh
- Delhi (National Capital Territory)
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu and Kashmir (Union Territory)
- Ladakh (Union Territory)
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- West Bengal
The list of union territories is as follows:
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Chandigarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
- Delhi (National Capital Territory)
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Puducherry
Rajasthan is the largest state in India by area, while Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state, How many states are there in India.
Who is known as the father of the nation of india
Mahatma Gandhi, whose full name is Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, is known as the ‘Father of the Nation’ in India. He was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat. Throughout his life, Gandhi adopted the principles of truth and non-violence, which made him a key leader in the Indian independence movement. After returning to India in 1915, he led several significant movements, including the Champaran Satyagraha and the Non-Cooperation Movement, which helped organize the Indian people against British rule.
The title ‘Father of the Nation’ was first given to him by Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose in a radio message from Singapore on June 4, 1944. This title was later recognized by the Government of India. However, he was already commonly referred to as ‘Bapu,’ a term of endearment used by his followers. Gandhi’s life and philosophy have inspired movements for human rights and freedom around the world. He was assassinated on January 30, 1948, after which Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru referred to him as ‘Father of the Nation,’ solidifying this title as a tribute to his legacy, Who is known as the father of the nation of india.
FAQs
What is the population of india
India’s population is approximately 1.4 billion (140 crores), making it the most populous country in the world. This number is continuously increasing, and it is estimated that the population will reach 1.42 billion by 2024. The population density in India is about 455 people per square kilometer, which ranks it among the most densely populated countries globally.
What is india’s rank in terms of area
India ranks seventh in the world in terms of area. Its total area is approximately 3,287,263 square kilometers. It is located in the southern part of Asia and shares its borders with several countries. Following countries such as Russia, Canada, the United States, China, Brazil, and Australia, India holds this position.
Which are the neighboring countries of India
India shares its land borders with several neighboring countries, including Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, and Bangladesh. These countries all have land boundaries with India. Additionally, India has maritime borders defined by its islands, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep.
Which country is the closest friend of india
India’s friendly countries include the United States, Russia, Japan, Australia, and France. These nations collaborate with India in various fields such as defense, trade, and technological development. Additionally, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) member countries like Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh are also considered close allies of India.
Which is the largest city of India
Mumbai is the largest city in India, located in the state of Maharashtra. It is not only the biggest city in terms of population but is also considered a center for economic activities. Mumbai is home to the Indian film industry, known as Bollywood, and serves as a major hub for financial institutions.
Which is the smallest city of India
Musafirkhana is considered the smallest town in India, located in the state of Uttar Pradesh. Its population is very low, and it is classified as a Nagar Panchayat. While there are many small towns and villages that are smaller in size, Musafirkhana is often referred to as the smallest city.
What was the first name of india
India’s ancient name was “Bharatvarsha.” This name comes from the Sanskrit word “Bharat,” which means “land” or “country.” In ancient texts, it was also referred to as “Jambudvipa.” Additionally, the Indian subcontinent was known by several other names such as “Arcadia” and “Hindustan.” What is India, Who discovered India.
